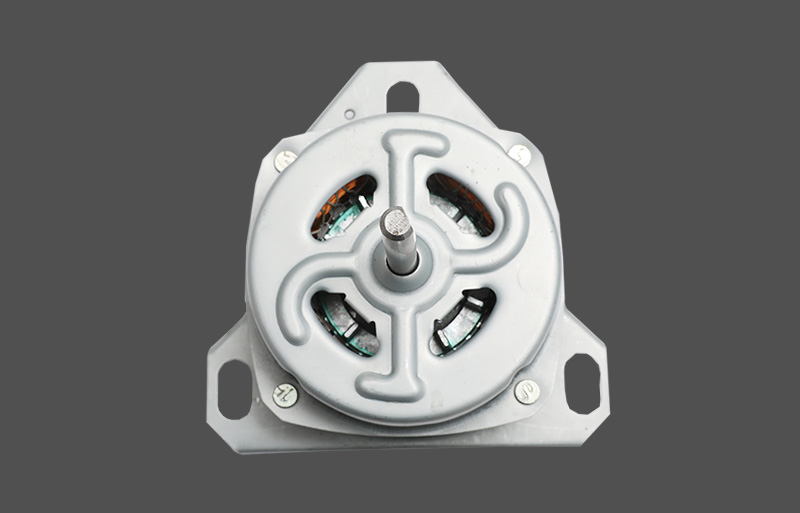
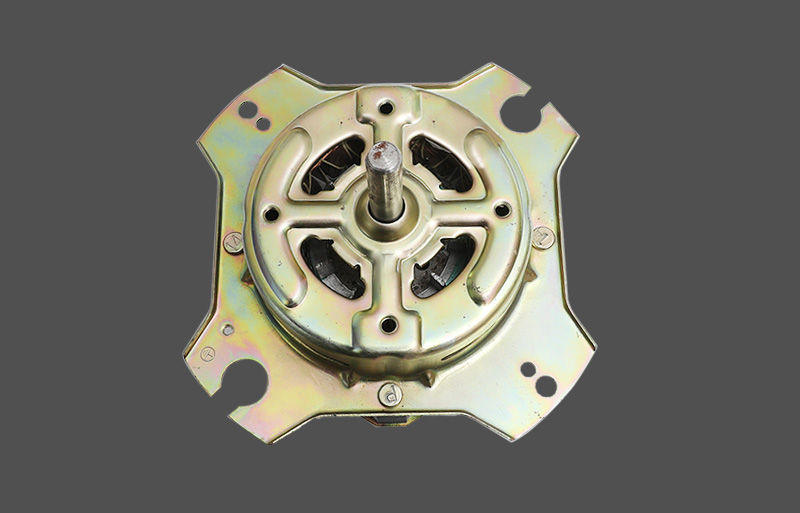
In the HVAC industry, the structural design of the fan motor determines the reliability, noise levels, and energy efficiency of the entire unit. Current market trends focus on the choice between the Resin-Packed Motor and the Metal-Shell Motor. These two motor types differ significantly in material science, manufacturing processes, and application scenarios.
Structural Process and Material Characteristics
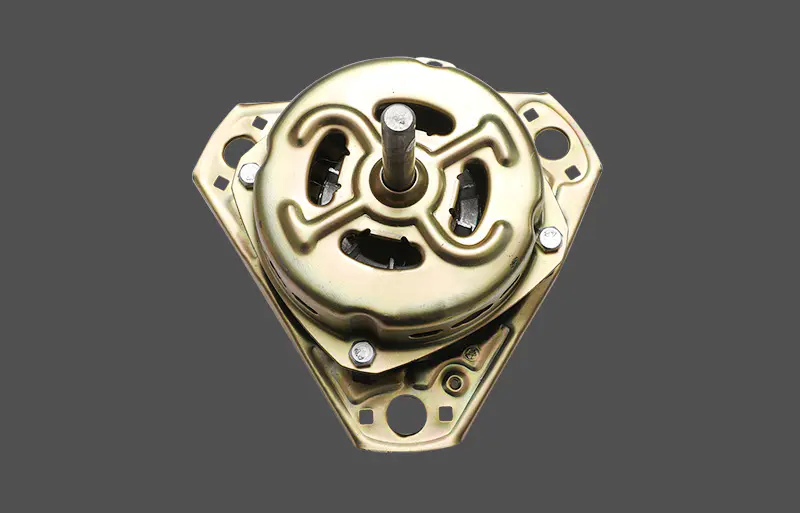
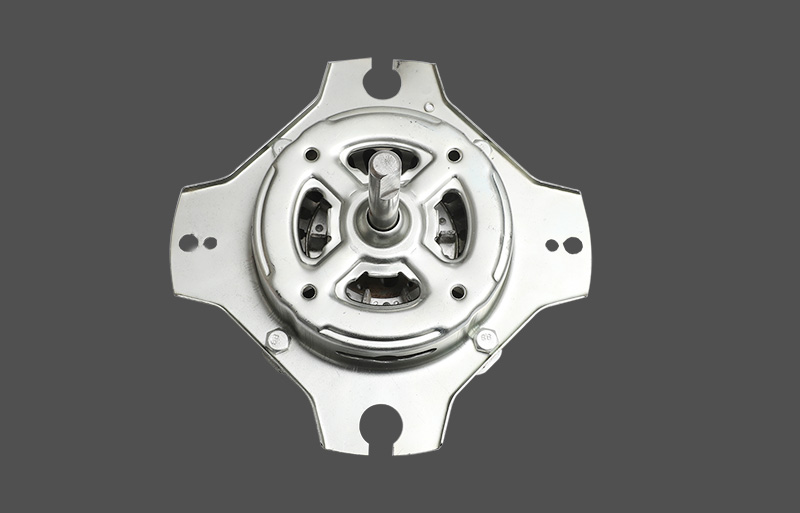
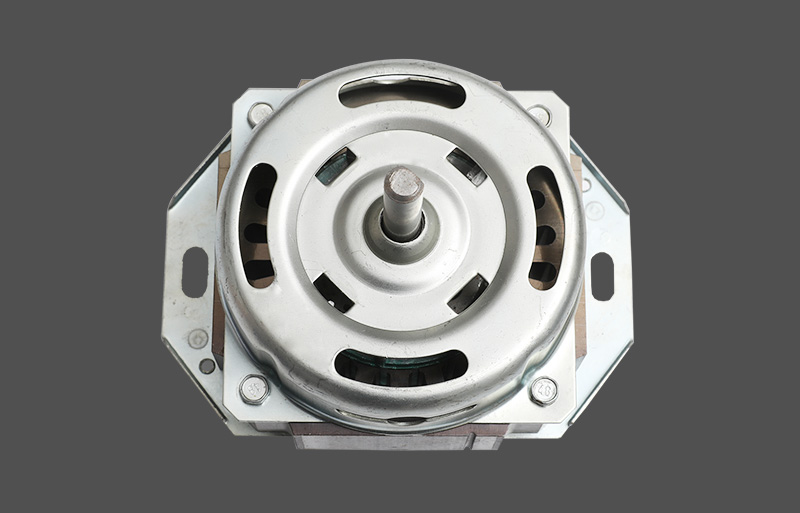
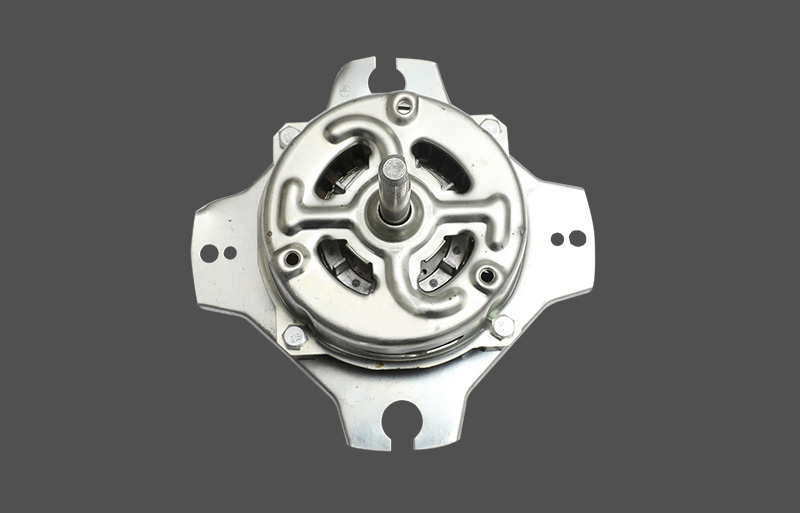
The Resin-Packed Motor utilizes unsaturated polyester resin or other high-performance thermosetting materials. Through a molding or injection process, the Stator windings, iron core, and thermal protector are encapsulated as a single integrated unit. This structure achieves a true "unibody" design. The Metal-Shell Motor uses a traditional housing made of stretched or cold-rolled steel sheets. The stator core is fixed inside the housing through press-fitting or fasteners. The exterior surface usually requires electrophoresis or spray coating to enhance its Anti-corrosion performance.
Electrical Insulation and Safety Performance
Regarding electrical safety, the Resin-Packed Motor possesses a natural advantage. Since the resin material itself is an excellent insulator, the encapsulation process eliminates the possibility of the stator windings contacting the external environment. Its Dielectric Strength is significantly higher than that of metal-shell motors. This design greatly reduces the risk of leakage current caused by humidity or dust, easily meeting Class B or Class F insulation standards. In contrast, the Metal-Shell Motor relies on Insulation Paper and frames between the windings and the metal casing. During long-term operation, if vibration friction or coating degradation occurs, the probability of a Ground Fault is relatively higher.
Noise Suppression and Vibration Control
For indoor units, Low Noise is the core metric for user experience. The Resin-Packed Motor leverages its dense encapsulation material to absorb and block Electromagnetic Noise generated during operation. The damping characteristics of the resin effectively suppress high-frequency vibrations of the Stator, leading to smoother operation. The Metal-Shell Motor, due to its rigid housing and internal micro-gaps, is prone to resonance effects. While this can be mitigated by adding Rubber Grommets, its mechanical and electromagnetic noise levels at high speeds are typically 2-3 dB(A) higher than those of resin-packed versions.
Thermal Dissipation and Energy Efficiency
Heat dissipation is a traditional strength of the Metal-Shell Motor. Metals have a high thermal conductivity coefficient, allowing heat generated by the windings to be quickly conducted to the surface and cooled by external airflow. This makes the metal-shell design effective for high-power applications, such as large central air conditioner outdoor units, which must withstand a heavy Thermal Load. While there were early concerns that Resin-Packed Motor materials would hinder heat dissipation, the use of thermally Conductive Plastics has narrowed this gap. The advantage of resin-packed motors lies in isolating the stator core from oxygen, preventing losses due to oxidation. From a long-term efficiency perspective, BLDC (Brushless DC) resin-packed motors offer highly precise efficiency control.
Environmental Durability and Adaptability
Performance under extreme conditions varies greatly between the two: Resin-Packed Motor: Offers superior waterproof, moisture-proof, and salt-spray resistance. Because the internal components are completely sealed, it effectively prevents Corrosion and short circuits even in high-humidity coastal regions. It is the ideal choice for high-end indoor units and high-performance outdoor units. Metal-Shell Motor: Better suited for applications requiring high mechanical strength. The metal casing resists external physical impact. However, in coastal environments, rust can still form at joints and screw holes even with anti-rust coatings, potentially leading to structural degradation over time.
Cost Structure and Manufacturing Trends
From a production standpoint, the Resin-Packed Motor requires a large initial investment in molds and high-precision injection processes. However, because it eliminates certain fasteners and complex insulation assembly steps, it offers cost-efficiency in large-scale mass production. Currently, global mainstream air conditioning brands have shifted toward resin-packed motors for their high-efficiency models, particularly those featuring DC Inverter technology. The Metal-Shell Motor maintains a presence in customized industrial air conditioners, fan coil units, and some entry-level split systems due to its flexible structural adjustment capabilities and lower costs for small-batch production.
Application Requirements and Selection
The choice depends on specific Application Requirements. For those seeking quiet operation, high insulation, and longevity in humid environments, the Resin-Packed Motor is superior. For high-power equipment emphasizing heat dissipation, physical strength, and cost sensitivity in small batches, the Metal-Shell Motor remains indispensable. In the Global HVAC supply chain, as BLDC technology becomes more prevalent, resin encapsulation has become an irreversible trend in motor design.